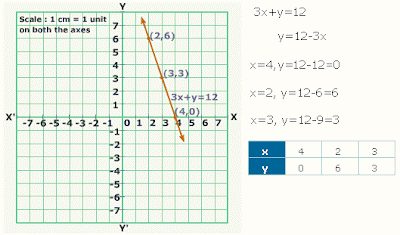
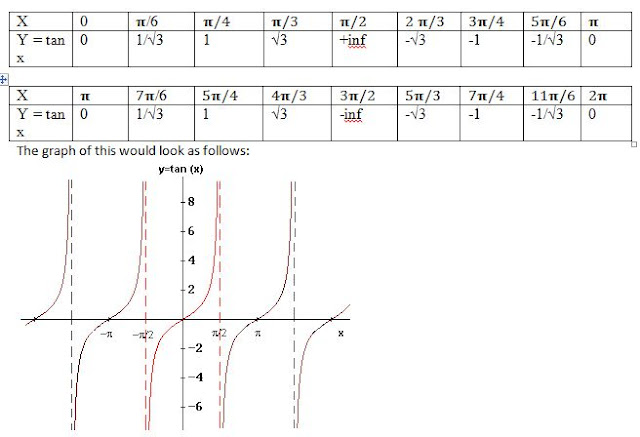
Mathematics is used throughout the world and it is an essential tool in many fields like natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. "Mathematics" is the Greek word its gives the meaning of learning, study, science, and additionally came to have the narrower and more technical meaning "mathematical study", even in Classical times.
Step by Step Math Solutions - Method to Solve:
There are many formulae abounded for solving math problem step by step One of the most important formula is P.E.M.D.A.S. It is nothing but the operations done in the problems solving in math. They are
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Step 1: First perform the operations inside a parenthesis.
Step 2: Now solve the exponents
Step 3: Then multiplication and division is done from left to right
Step 4: Then addition and subtraction is done from left to right
Step by Step Math Solutions - Example Problems:
Step by step math - Problem 1:
Solve the equation step by step
X + 6 = 8
Solution:
It is one step equation
Subtract 6 on both sides
X + ( 6 - 6 ) = (8 - 6)
X = 2
Step by step math - Problem 2:
Solve the equation step by step
4x + 2=18
Solution:
Subtract 2 on both sides
4x + (2 - 2) = 18 - 2
4x = 16
Divide by 4 on both sides
`(4x)/4` = `16/4`
X = 4
Step by step math - Problem 3:
Find the value of x step by step
6x - 8 = 4 x -10
Solution:
Subtract 4x from both sides of the equation
2x - 8 = - 6
Add 6 to both sides of the equation
2x = 2
Divide both sides by 2:
x = 1
The answer is x = 1
Step by Step Math Solutions - Probability Problems:
Step by step math - Problem 1:
A fair coin is tossed two times. What is the probability of getting at least one heads.
Solution:
Let A = be the event of getting at least two heads
Let S = Sample Space which refers to the total number of probable outcomes.
S = (HH, HT, TH, TT) =4
A = (HT, TH) =2
P (A) = `2/4` = `1/2`
The probability is `1/2` .
Step by step math - Problem 2:
Consider a die is rolled; calculate the probability of in receipt of odd numbers?
Solution:
There are six different outcomes 1,3,5,7,9,10,12,14,16,17,18
n (A) = 6, total number of odd numbers occur 6.
n (S) = 11, total number of outcomes is 11.
Probability of the event A happen = P (A) = n (A) / n(S) = `5 / 11` = 0.45.
Probability of the event A does not happen = P (A') = 1 – P (A) = 1 - 0.45 = 0.55.